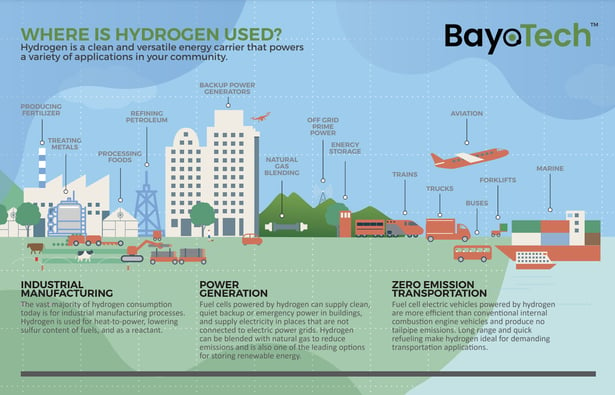
Hydrogen is a clean, versatile fuel that has the potential to play a major role in our clean energy future. It can be integrated into various sectors, from transportation to industrial processes, providing a viable alternative to fossil fuels. However, with any innovative technology, there can be misconceptions and concerns. In this blog, we'll debunk common myths about hydrogen.
We'll look at safety, job creation, environmental benefits, and fairness. Whether you're curious or concerned, we'll provide clear insights about hydrogen's potential and its place in a cleaner energy world.
Myth #1: Hydrogen is too dangerous to use.
While it's true that hydrogen is flammable, so are other fuels like gasoline and natural gas. Hydrogen is safer than what you might think. What sets hydrogen apart is its property of being lighter than air. In case of a leak, hydrogen disperses rapidly, minimizing the risk of combustion. Additionally, there has been a substantial amount of research and development focused on safety measures for hydrogen use. Over the decades, various safety codes, regulations, and standards have been established to ensure the safe handling, storage, and transport of hydrogen.
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Hydrogen is 14 times lighter than air. If released, hydrogen disperses quickly rather than pool at ground level, where accidental ignition presents a clear danger. | Hydrogen burns at a low radiant heat due to the absence of carbon. This lowers the risk of secondary fires. | Hydrogen is non-toxic. Leaks or spills do not contaminate the environment. | Thanks to decades of research and testing by private sector companies, the U.S. Department of Energy and other global entities have created safety codes and standards for everyone to follow for proper use of hydrogen systems. |
Key Safety Aspects of Hydrogen:
Lighter Than Air Dispersal: Hydrogen's 14-times lighter-than-air property allows it to rapidly rise in leaks, preventing ground pooling and contamination of water and soil.
Non-Toxic Leakage: Unlike fossil fuels, hydrogen leaks are non-toxic, posing minimal environmental impact compared to pollutants from fuel leaks.
Reduced Combustibility: Hydrogen's combustion level of 4% is higher than gasoline's 1.4%, making gasoline two to three times more flammable in the air.
Faster, Cleaner Combustion: Hydrogen's absence of carbon results in faster, lower radiant heat combustion, reducing the risk of secondary fires.
Established Safety Protocols: Decades of safe hydrogen use have led to rigorous safety protocols underpinned by global standards and research. Integrated leak sensors, ventilation, and flame detectors enhance safety during production. Transportation features leak suppression, venting, and stringent tank testing, exceeding traditional fuel vehicle crash standards.
Hydrogen Fueling Stations: These adhere to strict safety regulations like gasoline stations, reflecting proven safety standards.
Advanced Safety Features: Industry leaders like BayoTech employ cutting-edge safety controls such as emergency shut-off systems, leak detection, and remote monitoring, surpassing standard requirements.

Myth #2: Hydrogen production doesn't create jobs and will take jobs away from the oil and gas industry
There is a misconception that transitioning to a hydrogen-based economy will lead to job losses. However, the U.S. Department of Energy estimates that hydrogen has the potential to generate up to 2.5 million jobs by 2050. These jobs span a wide range of industries, including energy, manufacturing, and transportation. The federal government also incorporates requirements in all government funded hydrogen projects to meet specific wage and apprenticeship requirements. This helps stimulate the creation of good paying jobs and skill development.
Moreover, the transition presents an opportunity to repurpose skills from the oil and gas sector to the growing hydrogen industry. To support this effort, BayoTech has partnered with Ranken Technical College to develop training programs to educate the future hydrogen economy workforce. The inclusion of wage and apprenticeship requirements in government-funded hydrogen projects not only supports the creation of good-paying jobs but also fosters skill development and professional growth within the workforce. This approach aligns with broader efforts to ensure that economic growth is inclusive and benefits a wide range of individuals and communities.
Myth #3: Hydrogen is too expensive and not easily available.
The misconception that hydrogen is both costly and inaccessible overlooks the evolving hydrogen infrastructure and affordability. Contrary to this belief, a series of developments and initiatives show that hydrogen is becoming more adopted.
Growing Hydrogen Fueling Stations: The rising number of hydrogen fueling stations across various states, catering to thousands of vehicles, challenge the idea that hydrogen is scarce. These stations show its increasing availability and accessibility to the public.

Local Production Facilities: Local hydrogen production facilities contribute significantly to improving accessibility. This decentralized approach reduces transportation costs and enhances the availability of hydrogen as a fuel source.
DOE Hydrogen Earthshot: Initiatives like the DOE Hydrogen Earthshot are dedicated to driving down hydrogen production costs, aiming to make it a more affordable energy option for a broader audience.
Clean Hydrogen Tax Credits: The IRA's clean hydrogen tax credits play a crucial role in accelerating the transition towards clean electricity and decarbonizing industries. When strategically applied, these credits can pave the way for reliable and cleaner energy sources.
Myth #4: Hydrogen doesn't have any environmental benefits.
Hydrogen's clean-burning nature makes it a powerful tool for reducing emissions. When hydrogen is burned, it emits only water vapor, contributing to improved air quality and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. Furthermore, hydrogen's potential as an energy storage solution can bridge gaps in energy supply and support regions with limited access to energy resources.
Clean-Burning Emissions: One of hydrogen's most significant environmental benefits lies in its clean combustion. When hydrogen is burned, the only emission produced is water vapor, a stark contrast to conventional fuels that release harmful pollutants, including greenhouse gases, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds. By producing only water vapor, hydrogen combustion contributes to improved air quality and the reduction of harmful pollutants that contribute to climate change and health issues.
Reduced Reliance on Fossil Fuels: Hydrogen's potential to replace fossil fuels in various applications can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Transitioning from gasoline and diesel to hydrogen as a fuel source decreases the carbon footprint associated with transportation and industrial processes. This shift aligns with global efforts to curb emissions and fight climate change.
Energy Storage Solution: Hydrogen's versatility extends beyond being a fuel. It can serve as an efficient energy storage medium. This stored hydrogen can then be converted back to electricity using fuel cells or turbines when demand is high or renewable energy production is low. This capability addresses the intermittency of renewable sources and supports the stability of energy supply.
Energy Access for Remote Areas: Hydrogen's energy storage potential is particularly valuable for remote or off-grid areas with limited access to conventional energy sources. By storing excess energy as hydrogen, these regions can have a reliable and cleaner source of power, reducing their dependence on polluting diesel generators or costly energy imports.
Myth #5: Hydrogen production negatively impacts my community
The idea that hydrogen production inherently disturbs communities warrants a closer look. While it's true that hydrogen production facilities can emit potentially harmful substances, it's important to understand that these emissions are not uncontrollable.
Advances in technology and conscientious practices can effectively mitigate these concerns. By adopting conscientious practices and adhering to stringent environmental regulations, we can help ensure that hydrogen production facilities operate responsibly and minimize their impact on surrounding communities. This aligns with the principles of environmental justice, as it's essential to avoid disproportionately burdening marginalized communities with the negative consequences of industrial processes.
Emission Control Measures: Certain hydrogen production methods, such as Steam Methane Reforming (SMR), can release pollutants like nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide that contribute to air quality deterioration. However, these emissions can be managed through the implementation of pollution control technologies like Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR). SCR is a well-established method for reducing harmful pollutants in exhaust gases, particularly nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are common emissions from combustion processes.
Addressing Greenhouse Gases: Hydrogen production can also result in the release of greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2). However, it's important to note that these emissions can be curbed by employing sustainable practices and innovative technologies such as carbon capture and sequestration (CCS). Carbon capture and sequestration technology involves capturing CO2 emissions from industrial processes and power plants before they are released into the atmosphere and then storing or utilizing the captured CO2 in a way that prevents its contribution to climate change.
In addition to carbon capture and sequestration, another effective method of reducing the carbon footprint of hydrogen production is the incorporation of renewable natural gas (RNG) into the production process. RNG is produced from organic waste materials and captures methane emissions that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere. By using RNG as a feedstock for hydrogen production, industries can significantly reduce the net greenhouse gas emissions associated with the process.
Continuous Technological Advancements: Hydrogen production is a dynamic field that constantly evolves. With ongoing research and innovation, production technologies are becoming increasingly efficient and environmentally friendly. As advancements are made, the environmental impact of hydrogen production will become less and less.
Commitment to Environmental Responsibility
It's crucial to recognize that the concerns regarding hydrogen production's impact on communities are taken seriously by industry players and regulatory bodies. Efforts are being made to adopt greener practices, lessen emissions, and enhance the overall sustainability of hydrogen production processes.
Conclusion
As we work towards a cleaner, greener future, having the right information is crucial. Hydrogen has the power to change how we get energy, but we need to clear up misunderstandings first. Getting accurate and complete details about hydrogen can help communities and decision-makers make better choices. By showing that hydrogen is safe, can boost the economy, and is good for the environment, we can find better ways to get energy.
Stay on top of the latest developments in hydrogen technology to prevent being misled by hydrogen myths. Subscribe to the BayoTech blogs, newsletters and events, subscribe now.